Investors choose to build their businesses in Singapore for a variety of reasons. The simplicity of starting and operating enterprises is a significant driver. Another important driver is Singapore’s tax code, well-known for its low corporate and personal tax rates, tax breaks, lack of capital gains tax, one-tier tax structure, and numerous double tax treaties. The Singapore tax rate is determined by residence status. Check out our post on the country’s active tax rate.

Singapore Tax Rate 2024:
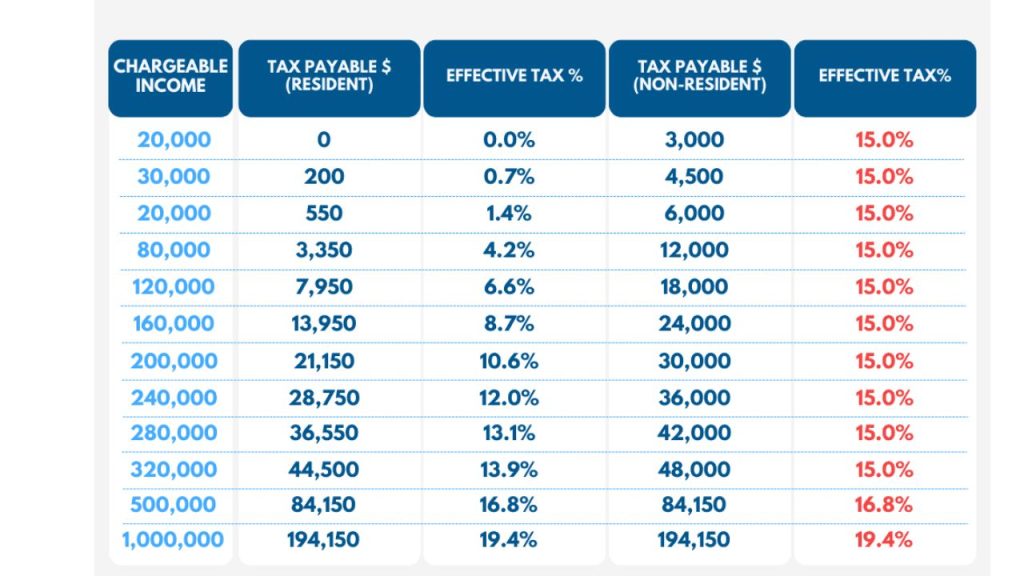
Income tax rates in Singapore vary for both citizens and foreigners. Personal tax rates start at 0% and are limited to 22% for Singaporeans. Outlanders pay a fixed rate that ranges between 15% and 22%. Income tax rates are notably dependent on an individual’s tax residence status.
An employee should begin paying income taxes while working and receiving the CPF. They are only required to pay the tax if their income exceeds the prescribed limit. After disclosing revenue and calculating current rates, the firm owner must pay the CTR-related taxes. Do not fear; share the Corporate Tax rates in the final section.
Singapore’s Tax Responsibility:
The (IRAS) is the government agency in charge of levies, collections, and enforcement of tax regulations in Singapore. IRAS aims to build a reasonable, straightforward tax system that reduces regulatory burdens and promotes economic progress. Furthermore, IRAS represents Singapore in international tax treaty discussions and assists the Ministry of Finance in developing tax laws.
The (IRAS) is the government agency in charge of levies, collections, and enforcement of tax regulations in Singapore. IRAS aims to build a reasonable, straightforward tax system that reduces regulatory burdens and promotes economic progress. In addition, the IRAS represents Singapore in international tax treaty talks and assists the Ministry of Finance in tax policy development.
- Low tax rates: While Singapore’s headline corporation tax rate is 17%, the effective tax rate for most Singapore firms is significantly lower, thanks to several tax benefits and deductions. The personal tax rate is progressive, from 0% to 22%.
- Dividends, capital gains, and inheritance are exempt from taxation under Singapore’s single-tier tax system. Furthermore, inheritances and capital gains are not subject to tax in Singapore.
- Territorial tax system: A territorial tax system taxes businesses depending on the location of their profits rather than their corporate headquarters. This implies that Singapore enterprises that make earnings overseas (also known as foreign source revenue) will not be subject to an extra Singapore tax. In other words, if your income was previously subject to taxation elsewhere, you will not incur any additional taxation in Singapore.
What Are Singapore Income Tax Rates?
Being a Singaporean does provide various tax benefits. Taxes on interest received from state banks with licenses are not due by citizens. On the other hand, foreign corporations will be subject to Singaporean corporate tax on interest income.
According to our facts, Singapore boasts the world’s lowest ITR. After determining your income tax due using our eligibility guidelines, you may wonder how to pay the income tax rates. The income tax filing deadline for all taxpayers is April 15, 2024. Dates have been constant over the previous few years.
Singapore’s current individual tax rates are as follows:
| Taxable income | Income tax rate |
| First S$20,000 | 0% |
| Next S$10,000 (up to S$30,000) | 2% |
| Next $S10,000 (up to S$40,000) | 3.5% |
| Next S$40,000 (up to S$80,000) | 7% |
| Next $S40,000 (up to S$120,000) | 11.5% |
| Next S$40,000 (up to S$160,000) | 15% |
| Next S$40,000 (up to S$200,000) | 18% |
| Next S$40,000 (up to S$240,000) | 19% |
| Next S$40,000 (up to S$280,000) | 19.5% |
| Next S$40,000 (up to S$320,000) | 20% |
| Above S$320,000 | 22% |
Eligibility:
Beneficiaries who meet the qualifying requirements may be recognized as tax residents for the 2024 assessment year.
- Individuals must be Singapore nationals residing in Singapore, except for brief absences.
- A foreigner who has built a permanent home in Singapore and obtained permanent residence.
- Alien immigrants who have worked in the nation for more than six months the previous year.
- Employees must earn at least $22,000 per year.
Individuals must be Singapore nationals residing in Singapore, except for brief absences.
A foreigner who has built a permanent home in Singapore and obtained permanent residence.
Alien immigrants who have worked in the nation for more than six months the previous year.
Employees must earn at least $22,000 per year.
How To File Income Tax In Singapore?
The official IRAS website allows you to file an income tax based on your income, family size, and immigration status. E-filing can be done using any of the methods described below. Remember, SingPass will be required to validate your digital identity on the myTax site.
- Just use SingPass or IUA to log in, then select “Individuals.”
- After a new page loads, select “File Income Tax Return.”
- Check all the pertinent information requested in the form now.
- The form has to be updated by recipients receiving any further aid.
- Complete the income source form. The application should also take the rental revenue into account.
- After you click “submit,” the electronic filing is completed. An acknowledgement receipt in the soft form will be sent to the applicant.
Taxpayers may visit the closest Post Office or IRAS office to make their income tax payment in person. You have two options for payment: cash or paper checks. Make sure you follow the officer’s instructions and supply all relevant information.
Singapore Corporate Tax Rate 2024:
Companies in Singapore are subject to corporate tax rates. Businesses are required to pay the government a certain amount of tax. Assume, for example, that a foreign firm makes $100,000, and the applicable corporation tax rate is 17%. In this case, the company will owe the government $17,000.
The Singaporean government receives a sizable portion of its income from this tax. Enforcing CTR made sure that companies contributed equitably to the state’s economy and society so that it would run smoothly. It is essential to submit CT on time to avoid fines from the government.
Both domestic and international enterprises receive the same CTR. The corporate tax rate for businesses established under “Ltd” and overseas companies with a branch in Singapore is 17% for 2024. Recipients pay different taxes according to the income they earn within the country. Singapore’s income tax system does not apply to Singaporeans who work overseas, making them an exemption.
The following are Singapore’s current corporation tax rates:
- Corporate profit tax rate up to 300,000 SGD: 8.5% is the effective tax rate.
- A 17% tax rate is applied to company earnings of over 300,000 SGD.
- Tax rate on capital gains that the business has amassed: 0%
- 0% tax is applied on dividend payments made to shareholders.
- A 0% tax rate is applied to income originating outside of Singapore.
- Income originating abroad brought into Singapore is subject to a tax rate ranging from 0% to 17%.
Tax Types in Singapore:
- Income tax is levied on both corporate and individual income.
- Property taxes are levied against property owners according to the anticipated rental income from their holdings.
- Since February 15, 2008, estate duty has been eliminated.
- Other than import charges, motor vehicle taxes are levied on motor vehicles. Road congestion and automobile ownership are the two main goals of these levies.
- Customs and Excise charges: Singapore enjoys shallow import and excise charges because it is a free port. Liquor, tobacco, and petroleum goods are subject to excise taxes. Additionally, import tariffs are applied to only a few items. Petroleum goods, tobacco, alcohol, and motor vehicles are the primary targets of the duties.
- The GST, or goods and services tax, is a consumption tax. When money is spent on products or services—including imports—the tax is paid. In many other nations, Value Added Tax (VAT) is another name for this type of indirect tax.
- Betting taxes are levied on sweepstakes, betting, and private lotteries.
- Legal and business papers about stocks, shares, and real estate are subject to stamp duty.
- Others: The primary taxes are the airport passenger service charge and the foreign worker levy. The purpose of the foreign worker tax is to control the hiring of foreign labourers in Singapore.
Read Also – The World’s Ten Biggest Economies As of 2024: What is GDP?